A hard drive, sometimes abbreviated as hard disk, HD, or HDD, is a storage medium that is installed internally in a computer. The hard drive is connected directly to the disk controller of the computer's motherboard.
The drive contains one or more platters in an airtight enclosure. Data is written to the disks using a magnetic head, which moves quickly over the disks as they spin.
Internal hard drives reside in a drive bay that connects to the motherboard with an ATA, SCSI, or SATA cable.
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a new generation of storage medium used in computers. SSDs replace traditional mechanical hard drives with flash memory that is significantly faster. Older storage media with hard drives run slower, often causing your computer to run slower than it should. SSDs speed up computers significantly due to their low read access times and fast data processing capacity.
In this article you will find detailed information on how to get one You can format your hard drive or USB stick via Windows Command Prompt.
Format disk via Command Prompt
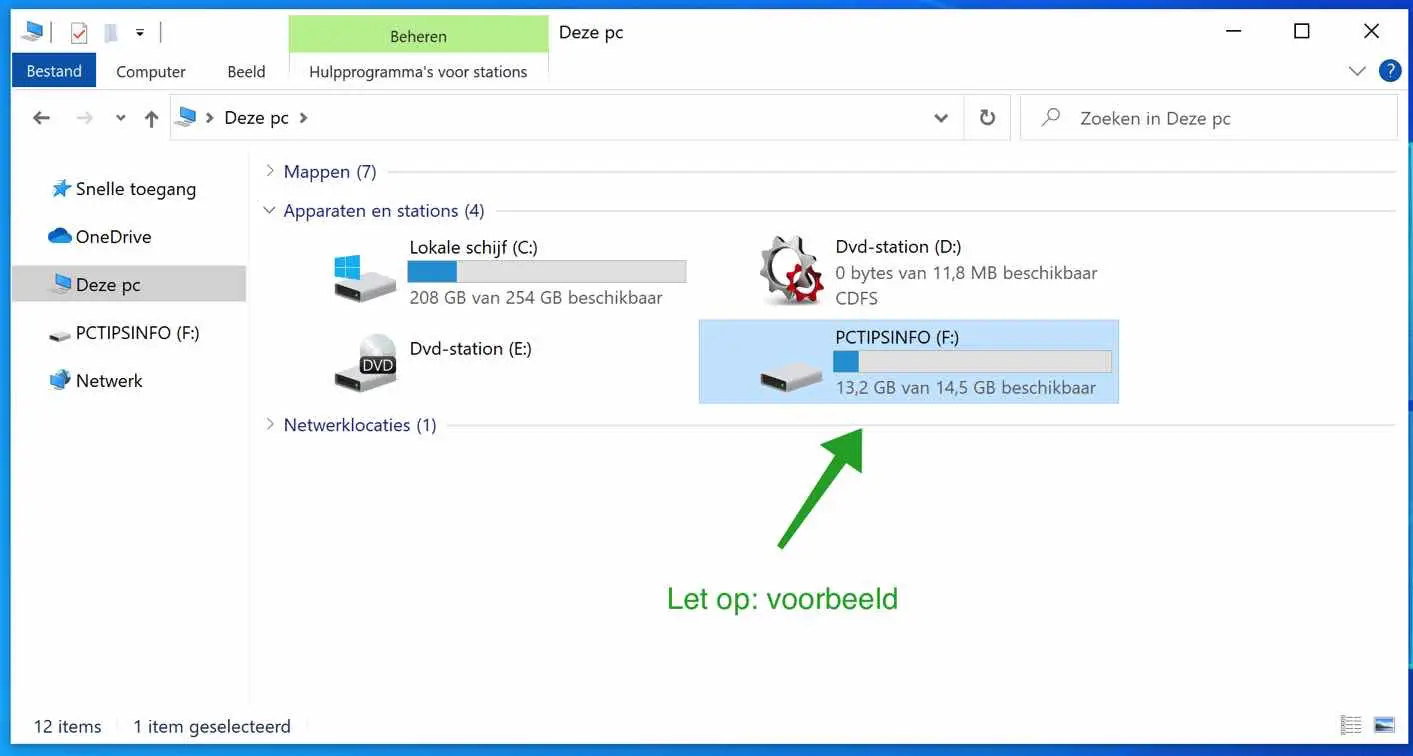
To get started, it is important to first check which drive letter is assigned to the medium you want to format. You can do this in the following way.
Open Windows Explorer, click My Computer and check the assigned drive letter.
If you have checked which drive letter is assigned to the volume then you can Open Command Prompt.
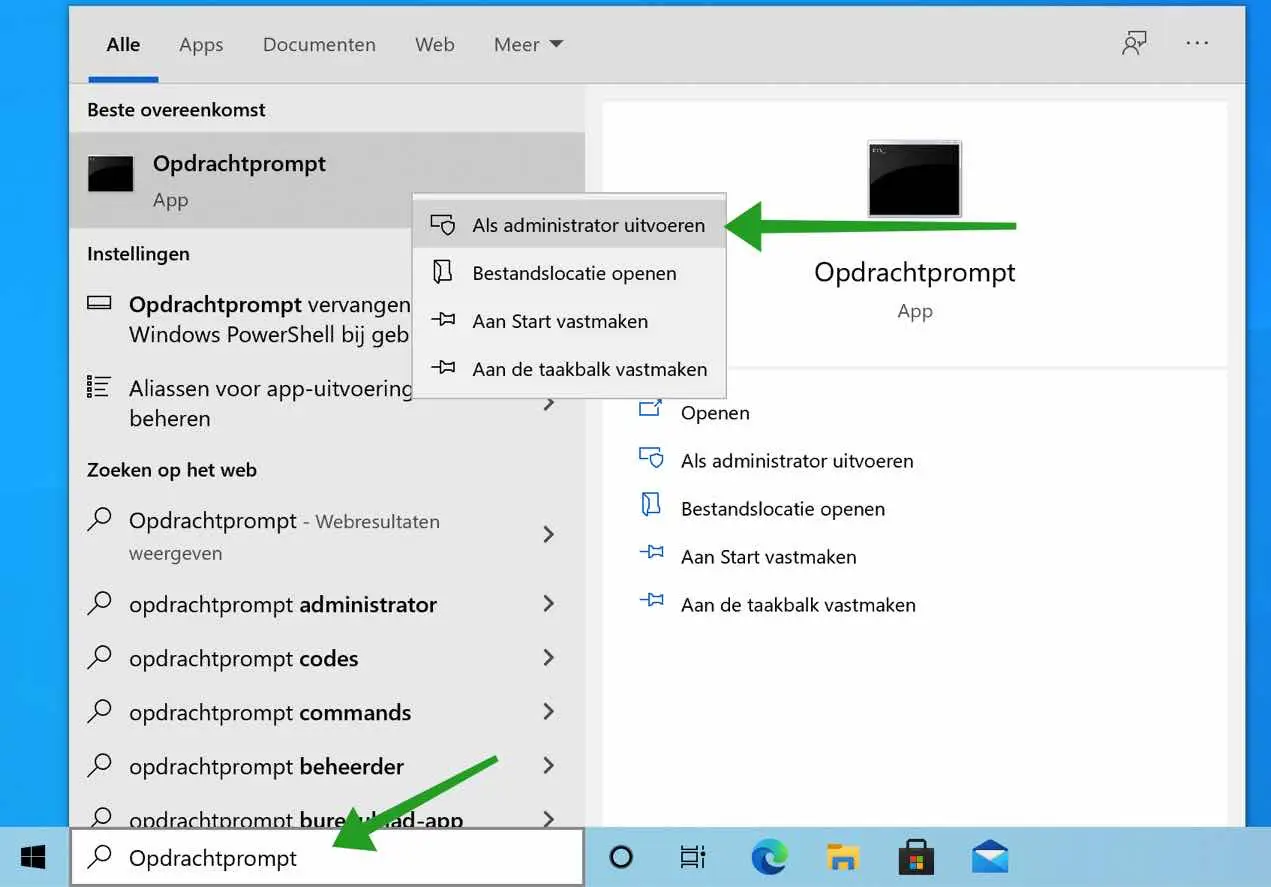
In the Windows search bar type: Command Prompt.
Right-click on the Command Prompt result and choose Run as Administrator.
Format disk
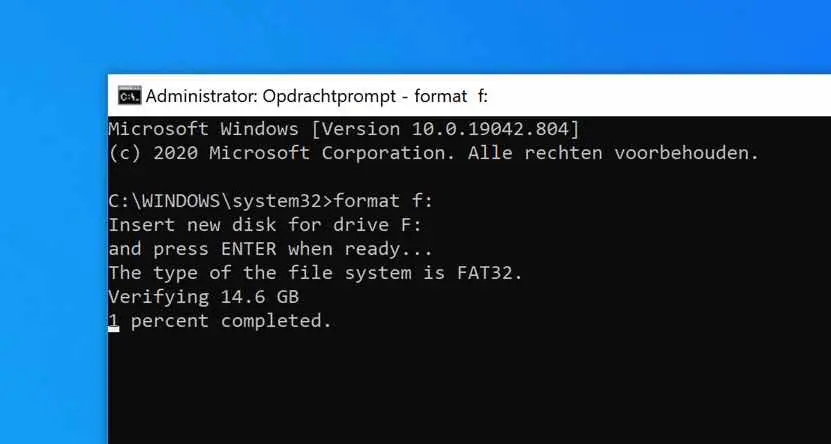
In the Command Prompt type the following command to format the drive. Note I use drive letter F as an example. You must use your previously determined drive letter!
format F:
The drive will now be verified first and then formatted. This whole process can take a while.
Quickly format disk
To speed up the formatting process, you can use the Quick Format argument.
A quick format can overwrite all files on the hard drive, but it won't erase them completely. If you use special software, the old files can be recovered.
In Windows gives you the option to create a disk can be quickly formatted in FAT or NTFS format.
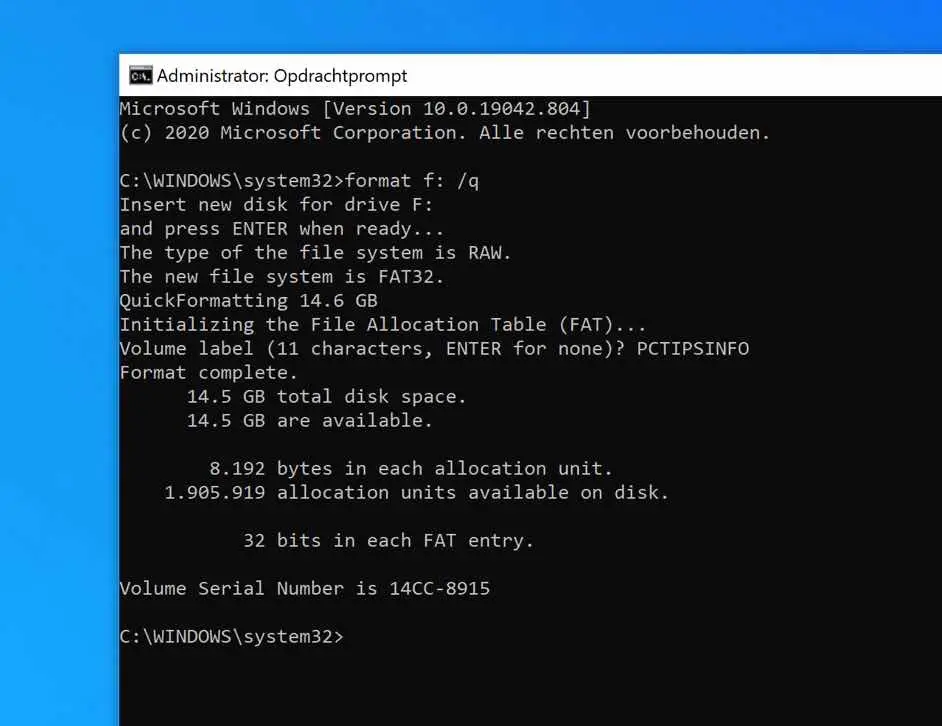
You can quickly format a hard drive with the following command: /q. The complete command then becomes.
format F: /q
Format disk as NTFS exFAT or FAT32
If you are going to format a disk, you can choose from different file systems. If you use the standard format command the disk will be formatted in FAT32 file system. You still have a choice NTFS of exFAT.
To choose a specific file system from the Command Prompt, use the /FS:FILE SYSTEM argument.
This is what it looks like as a total format command.
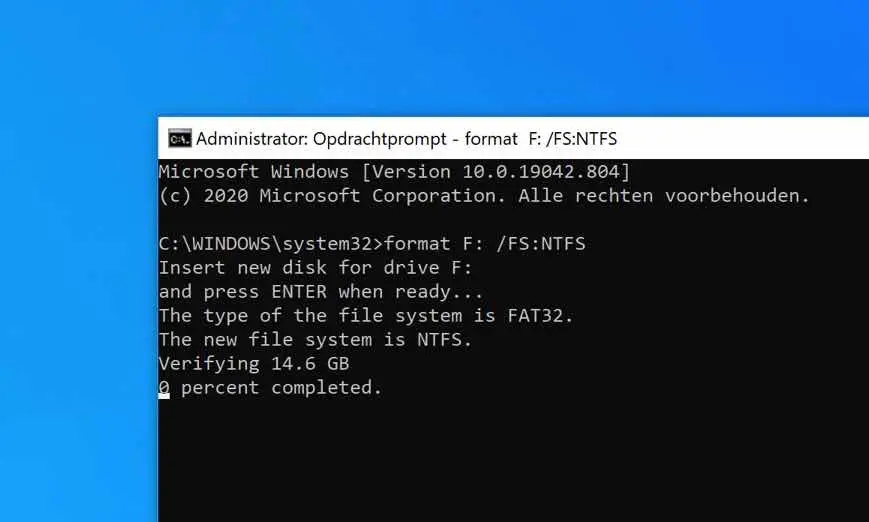
format F: /FS:NTFS
format F: /FS:FAT32
format F: /FS:EXFAT
Completely format disk by overwriting data several times
To ensure that no one can ever retrieve the data on the hard drive, USB stick or any other medium, you can use the following command: /p:NUMBER.
The total command will then look like this.
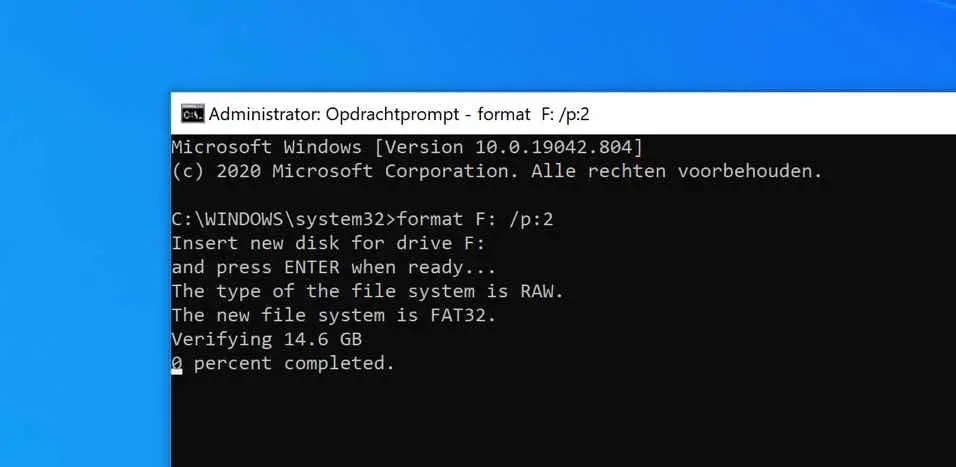
format F: /p:2
By using the /p:2 argument you indicate that all sectors on the hard disk should be overwritten twice with null. You can customize two according to your wish. Please note that formatting this way takes a very long time.
This makes retrieving data from the drive next to impossible as far as I know.
It is always possible to combine the format commands I have covered in this article to output your desired file system and type of format.
I hope this helps you. Thank you for reading!