If you regularly use a specific location on your hard drive, it may be useful to turn this folder into a virtual drive. You are essentially creating a shortcut from the location or your hard drive to a drive letter.
You can then easily access the location on your hard drive directly from Windows Explorer or a Command Prompt. This saves time but can also be useful in a work-related (for example a domain) environment.
When a folder is mounted as a virtual hard drive, you can access its contents from the virtual drive. Any changes made to the files or folders within the folder are saved to their actual location.
That means, the folder is mounted as a virtual drive, but physically the location is still the actual folder location. By default, the virtual hard drives that are created are only available for the current user session. They are automatically deleted when you log out, restart the PC or shut down the PC.
Using Command Prompt commands such as diskcomp, diskcopy, recover, format, label, and chkdsk do not work on these virtual hard drives. Keep this in mind when you create a virtual disk and process it in a script.
Create and manage virtual disk in Windows
Create virtual hard drive
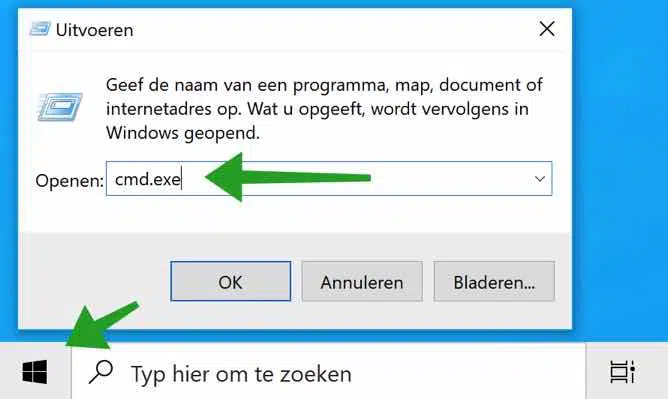
To create a virtual disk directly, open Command Prompt. Right-click on the Windows start button. In the menu click on Run. In the run window type: cmd.exe
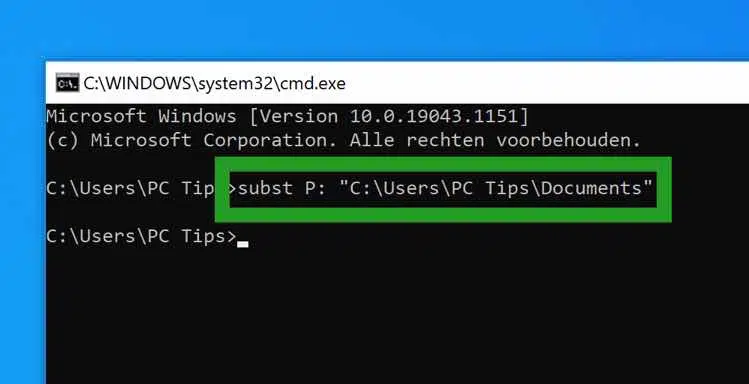
As an example, in the Command Prompt window, type the command:
subst P: "C:\Users\PC Tips\Documents"
Substance is the program that ensures that the virtual disk can be created.
P: is the drive letter.
“C:\Users\PC Tips\Documents” is the path. Be careful to use double quotes if the path contains spaces. In principle, it is best to always use double quotes, even with a path without spaces.
Of course the above is an example. You can use this to create a virtual drive letter yourself. You cannot use drive letters that are already in use.
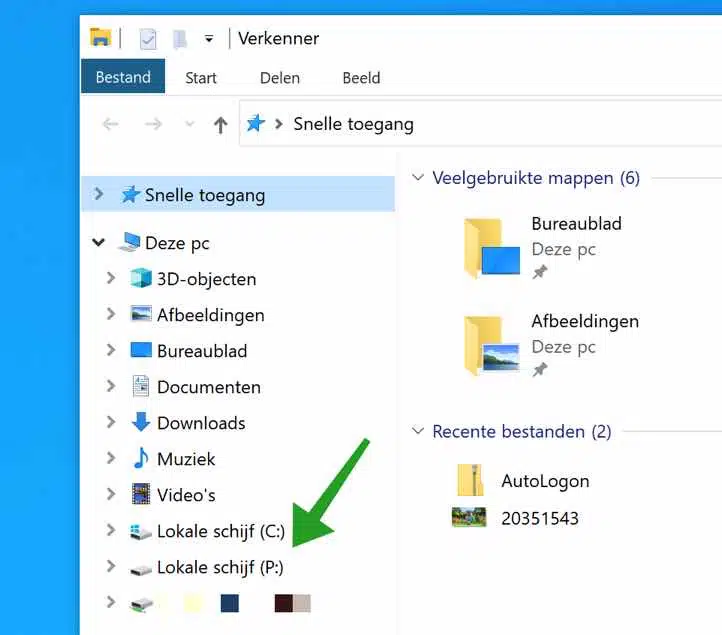
In Windows Explorer, you will see a new drive letter after creating a virtual hard disk with the “subst” command. This disk is referred to as “local disk”.
Remove virtual hard drive
If you want to delete a created virtual hard drive, you simply need to delete the drive letter.
Right-click on the Windows start button. In the menu click on Run. In the run window type: cmd.exe
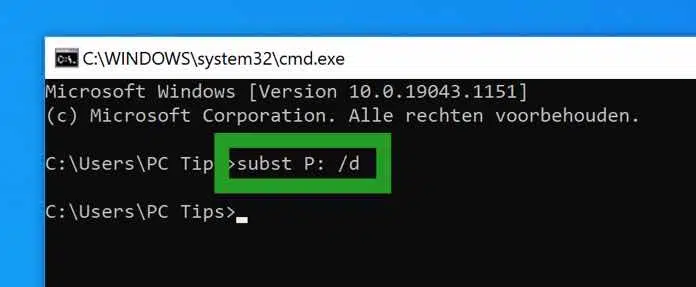
As an example, in the Command Prompt window, type the command:
subst P: /d
Substance is the program to manage the drive letter.
P: is the drive letter you wish to delete.
/d is the argument that means “delete”.
The above is again an example.
Show virtual hard drive
You will see a virtual (mapped) hard drive in Windows Explorer on the left side of the shortcut menu. You can also query the virtual hard drives via the Command Prompt with the subst command.
Right-click on the Windows start button. In the menu click on Run. In the run window type: cmd.exe
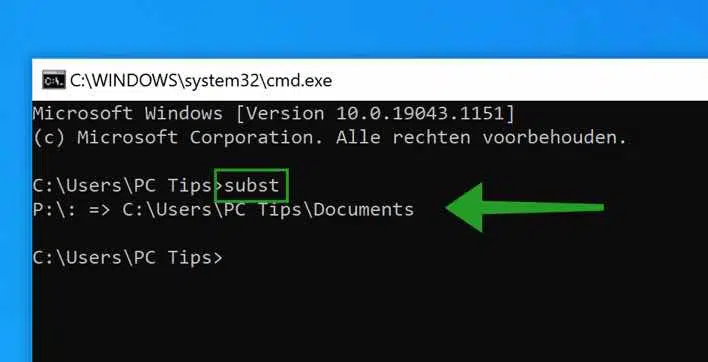
In the Command Prompt window, type the command:
subst
You will then immediately see an overview of the created virtual disks.
Lees meer: defrag hard drive.
I hope this helped you. Thank you for reading!