A full backup of Windows 11 is crucial computer problems. If problems arise due to broken hardware, viruses, or a failing computer system, you can always restore a full system backup.
There are several ways to make a system backup. Most people are familiar with a backup via the settings in Windows 11. You can configure and start this via the settings.
Less well known is the tool “wbadmin”. WbAdmin is a tool to create a full system backup via Command Prompt or Windows Terminal. You can use WbAdmin on its own or you can deploy it in a server and workstation environment via scripting.
There are several parameters you can apply to wbadmin. Below you will see the various parameters with information about the parameter in question. Some technical knowledge required.
-backupTarget
Specifies the storage location for the backup. Requires a hard disk drive letter (e.g.: E:), a volume GUID-based path in the format \\Volume\{GUID}, or a Universal Naming Convention (UNC) path to a remote shared folder (\ \ \ ). So external media or an external network location is always needed to store the backup.
-include
Specifies a comma-separated list of items to include in the backup. You can include multiple files, folders, or volumes. Volume paths can be specified using volume drive letters, volume mount points, or GUID-based volume names.
If you use a GUID-based volume name, it must be terminated with a backslash (\). You can use the wildcard character (*) in the file name when specifying a path to a file. The -include parameter may only be used in combination with the -backupTarget parameter.
-exclude
Specifies a comma-separated list of items to exclude from the backup. You can exclude files, folders, or volumes. Volume paths can be specified using volume drive letters, volume mount points, or GUID-based volume names.
If you use a GUID-based volume name, it must be terminated with a backslash (\). You can use the wildcard character (*) in the file name when specifying a path to a file. The -exclude parameter may only be used in combination with the -backupTarget parameter.
-nonRecurseInclude
Specifies the non-recursive, comma-separated list of items to include in the backup. You can include multiple files, folders, or volumes. Volume paths can be specified using volume drive letters, volume mount points, or GUID-based volume names.
If you use a GUID-based volume name, it must be terminated with a backslash (\). You can use the wildcard character (*) in the file name when specifying a path to a file. The -nonRecurseInclude parameter may also only be used in combination with the -backupTarget parameter.
-nonRecurseExclude
Specifies the non-recursive, comma-separated list of items to exclude from the backup. You can exclude files, folders, or volumes. Volume paths can be specified using volume drive letters, volume mount points, or GUID-based volume names.
If you use a GUID-based volume name, it must be terminated with a backslash (\). You can use the wildcard character (*) in the file name when specifying a path to a file. The -nonRecurseExclude parameter may only be used in combination with the -backupTarget parameter.
-allCritical
Specifies that all critical volumes (volumes that contain operating system state) should be included in the backups. This parameter is useful if you are backing up for bare metal recovery. It should only be used if -backupTarget is specified, otherwise the command will fail. Can be used with the -include option.
Optional: The target volume for a critical volume backup can be a local drive, but it cannot be any of the volumes included in the backup.
-systemState
Creates a backup that contains the system state, in addition to any other items you specified with the -include parameter. The system state includes boot files (Boot.ini, NDTLDR, NTDetect.com), the Windows registry, the SYSVOL (Group Policy and Login Scripts), the Active Directory and NTDS.DIT on domain controllers, and, if the Certificate Service is installed, the Certificate Store.
If the server has the Web server role installed, the IIS metadirectory is also included. If the server is part of a cluster, information about the Cluster Service is also included.
-noVerify
Indicates that backups stored on removable media (such as a DVD) are not checked for errors. If you do not use this parameter, backups stored on removable media will be checked for errors.
-user
If the backup is saved to a remote shared folder, specify the username with write permissions to the folder.
-password
Specifies the password for the username specified by the -user parameter.
-noInheritAcl
This applies the Access Control List (ACL) permissions corresponding to the credentials specified by the -user and -password parameters to WindowsImageBackup (the folder containing the backup).
To access the backup later, you must use these credentials or be a member of the Administrators group or the Backup Operators group on the computer with the shared folder. If -noInheritAcl is not used, the remote shared folder's ACL permissions are applied to the folder by default so that anyone with access to the remote shared folder can access the backup.
-vssFull
Performs a full backup using the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS). All files are backed up, the history of each file is updated to show that it was backed up, and the logs of previous backups can be truncated.
If this parameter is not used, wbadmin start backup will create a copy backup, but will not update the history of the files being backed up.
Note: Do not use this parameter if you are using a product other than Windows Server Backup to back up apps that are on the volumes included in the current backup. This can disrupt the incremental, differential, or other types of backups that the other backup product makes, because the history they use to determine how much data to back up may be missing and they may need to perform a full backup unnecessarily. can perform.
-vssCopy
Performs a copy backup using VSS. All files are backed up, but the history of the files being backed up is not updated, so you retain all information about which files were changed, deleted, etc., as well as any app logs.
Using this type of backup does not affect the sequence of incremental and differential backups that can occur independently of this copy backup. This is the default value.
Please note: A copy backup cannot be used for incremental or differential backups or restores.
-quiet
Last. Quiet executes the command without messages to the executor.
Create full system backup of Windows 11 with WbAdmin
To perform a full system backup to removable media, such as an external hard drive or USB flash drive, perform the following.
Connect the removable media to your PC. Verify which drive letter is assigned to the device, and that the removable media contains enough total disk space to accommodate a full backup.
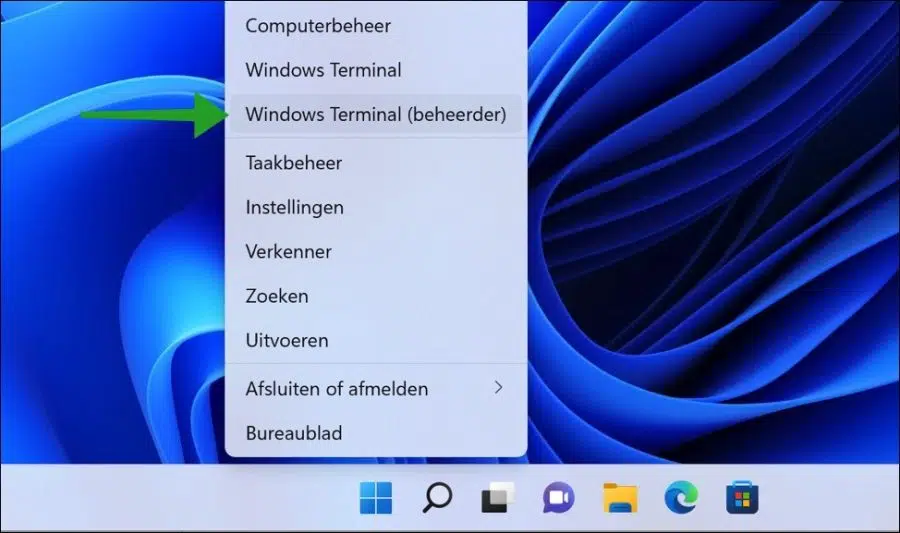
Right-click on the Start button. In the menu, click on “Windows Terminal (administrator)”.
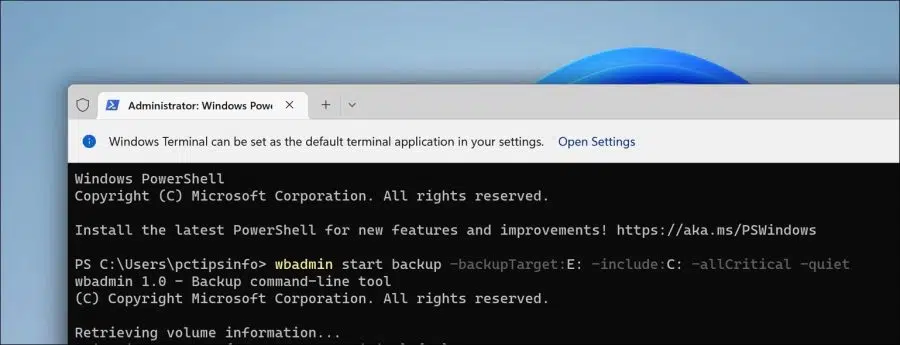
Now enter the following command:
wbadmin start backup -backupTarget:E: -include:C: -allCritical -quiet
It is important that you use -backupTarget:E: changes to the drive letter assigned to the device you want to back up to. This is the external hard drive or the USB device.
Using the example above, you will make a full backup from the C: drive to the E: drive. If you want to include other drive letters in the backup, add them separated by a comma to “-include”. For example -include:C:,D:,E:,F:
By passing -allCritical as an argument, you specify that all critical volumes (volumes that contain the operating system state) should be included in the backups.
After making the backup via Wbadmin you can use the advanced boot options restore the system backup.
Also read: Back up files on your computer to Google Drive
I hope this helped you. Thank you for reading!